How to keep the Eyes Healthy?
- The eyes are extremely delicate part of the body and hence need good care. This care begins at birth and continues throughout the life span. Infections of the eye spread very rapidly, if proper care is not taken. Ways to maintain eye health are as follows:
- Keep eyes clean by washing them with clean water. Washing eyes at bedtime is very good as it removes the dirt and dust collected throughout the day.
- Do not work in poor light. Reading in poor light can strain eyes.
- Always use a clean cloth to wipe eyes. Do not use saris, dhotis, or sleeves of clothes to wipe eyes. These may cause serious infection in the eyes. Eye diseases such as conjunctivitis and trachoma spread by this way.
- Each person should use a separate cloth, towel or handkerchief for wiping eyes. If one eye is already infected, use a separate clean cloth for each eye.
- Avoid the glare. Do not stare at the sun and other bright objects.
- Never walk out in the sun without sunglasses.
- Eat a diet rich in Vitamin A and appropriate breastfeeding by mothers (colostrum is rich in Vitamin A).
- Do follow the 20-20-20 rule of eye care when using a computer/laptop, mobile phone, or watching television. Every 20 minutes, refocus your eyes for 20 seconds to an object located at least 20 feet away.
- Report any eye infection to a health worker. Do not use home remedies for eye medication. Do not use medicines given by road-side medicine sellers. These may not help and may even cause blindness.
- Eye drops and eye ointment only provided by a Medical doctor should be used. Do not use any eye medicine without any medical prescription.
- Patient with eye infection should avoid going in swimming pools and visiting public places
- If you have an eye problem go to your nearest health care facility as soon as possible. Go immediately if you have an eye injury, if your eyes are painful or if your vision suddenly becomes poor.
- If you have hypertension or diabetes, have a complete eye examination at least once a year, and check your blood pressure and blood sugar regularly.
- If you have a relative with glaucoma, have an eye examination for glaucoma at least once a year.
- Use protective eyewear when working with objects that might damage your eyes: welding, chemicals, metal or wood, farming season, etc.
- If chemicals or substances that burn or sting come into contact with your eye, immediately rinse your eye with clean water for at least 15 minutes and visit the nearest hospital.
- If you have problems seeing small nearby objects or when reading, you may need glasses for near work.
- Keep the eyelashes clean. Eyelashes of individuals might have ticks/lice/mites or their eggs. These individuals should be referred to the nearest hospital. Provide them tips for maintaining eye hygiene.
Refrective Error
In normal vision, light rays from an object focus on the retina (emmetropia). Alternatively, in the presence of a refractive error, the light rays get focused in front or behind the retina causing blurred vision. Under normal conditions, as the eye ball grows in size from infancy to adulthood, there will be a corresponding change in curvature of the cornea and the lens, enabling the eye to remain emmetropic , at all ages.
These refractive errors can be classified as myopia (near sightedness) and hyperopia (far sightedness).
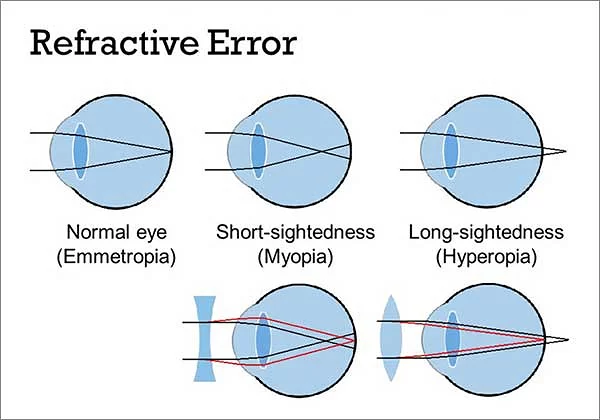
What is hyperopia?
In hyperopia or far sightedness, the light rays from an object form an image behind the retina.
- Children with hyperopia
- Find difficulty in reading, writing and looking at nearby objects
- Eye strain while trying to read for long hours
- May have squint (crossed eyes)
What is myopia?
In myopia or near sightedness, the light rays from an object form an image in front of the retina.
- Children with myopia
- Have defective vision for distance and clear vision for near
- Shrink their eyes while trying to see ditant objects
- Hold books close to their face while reading
- Children with the above conditions may also have Pain, watering or burning sensation in the eyes, rub their eyes constantly or blink frequently, because of the eye strain which they experience all the time
- Headache in the forehead region intensified in the evening
- Recurrent swelling in the eye lids
When should eye sight be checked?
- Eyesight of children and adults should be checked as per follows in nearby health facility where Eye doctor/Eye specialist/Ophthalmic Assistant is available:
- When the child starts going to school at entry level. After that once in a year.
- For children wearing glasses: once every six months.
- For adults: When they turn 40 years, especially for near vision. Treatment
- Correction using spectacle is the best option available. Though children may initially refuse to accept glasses, they will become fond of them once they realise they can see better with them on.
- An eye checkup and change of glasses if necessary,has to be done once in 6 months for children under 5 years of age and once a year thereafter. Children older than 15 years can use contact lenses if they don’t want spectacles. Those over 18 to 20 years of age with stable power also have the option of LASIK, a laser refractive surgery apart from contact lenses.
Cataract
Cataract is defined as opacity in the lens, which interferes with vision. Cataract is the most common age-related eye disease and is also the most treatable cause of vision loss in older adults. Largely, adults more than 50 years, can be affected by it which means it is an age- related condition which occurs due to degeneration and ageing process but it may also be present congenitally in children. Cataract can also
occur due to other conditions like Diabetes Mellitus(DM) in adults, or after an eye injury, inflammation or long-term steroid use.
- HEALTH EDUCATION MESSAGES FOR THE COMMUNITY ON CATARACT
- It is normally seen in elderly people and is a result of ageing. However, it can also occur in younger age groups and in children. Adult persons with diabetes are more likely to develop cataract at an early age.
- It cannot be cured by putting any eye drops/eye ointment. Cataract can be cured only with eye surgery.
- The eye procedure commonly involves taking out the affected lens from the eye and replacing it with a new artificial lens so that vision can be restored to normal.
- This procedure for correction of cataract is a safe and commonly done, but only in a recognized hospital with eye specialist.
- Under National Programme for Control of Blindness and Visual Impairment (NPCB & VI), Government Eye Hospitals and Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs) provide free surgeries to affected persons.
- In adults that have cataract due to ageing, both eyes may be affected and treatment may be required for both the eyes.
Post Cataract Surgery Advice
- The operated eye should be protected with an eye shield.
- The operated eye should be protected from bright light, TV screen, mobile, computer, dust, smoke, smoke from chullas and jerks (quick, sharp, sudden movement) for time period as suggested by the doctor. Need for using protective eye wear such as dark eyeglasses during daytime will be advised by the doctor.
- The eye doctor will advise the patients for putting frequent eye drops in daytime and eye ointment at night to the operated eye. These should be done correctly for the period prescribed.
- The patient should not rub the operated eye.
- The patient should not put water into the operated eye but should maintain hygiene around the eyes by cleaning it. The area around eyes can be cleaned by using cotton. Take a bowl of water and cotton, boil it and let it cool. Now, cotton can be used to put water around eyes. This can be done every morning by the patient after the surgery.
- Avoid having a head bath for at least 1month after cataract surgery.
- The patient should not sleep on the same side as the operated eye atleast for one week.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects/ exercises for 4-6 weeks and avoid applying kajal/any eye make-up for at least 4 weeks.
- Normal balanced diet should be taken by the patient after the surgery.
- After the eye surgery is done, it is important for the patient to visit and consult eye doctor after one week of operation and then after one month of operation.
- If there are any complaints in the operated eye like redness, pain or poor vision, the patient should contact the eye surgeon/eye doctor immediately.
- Patients after the surgery may require spectacles depending on type of lens used in the eye.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of related eye disorders that cause damage to the optic nerve that carries images from the eye to the brain. In most cases, glaucoma is associated with higher-than-normal pressure inside the eye and changes in field of vision. If untreated or uncontrolled, glaucoma first causes peripheral vision loss and eventually can lead to blindness (known as ‘silent thief’ of vision). It is usually detected late when 40% of the vision is lost.
- Glaucoma cannot be cured, it can only be controlled.
- Vision loss due to glaucoma cannot be recovered.
- Early detection and treatment of glaucoma before it cause significant visual loss is ideal way to control the disease.
- It is essential that persons above 40 years of age have their eyes examined periodically to detect glaucoma early.
- If any one of the family member has glaucoma, its advisable that rest of the family members have their eyes examined.
- Once diagnosed as having glaucoma, patient should be committed for life long treatment and periodical eye check up.
- Drugs prescribed should be regularly used at specific time, to ensure round the clock pressure control.
- Medication may cause few undesired effects. In the event of any adverse effect, the patient must approach the ophthalmologist immediately for alternate treatment.
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY

