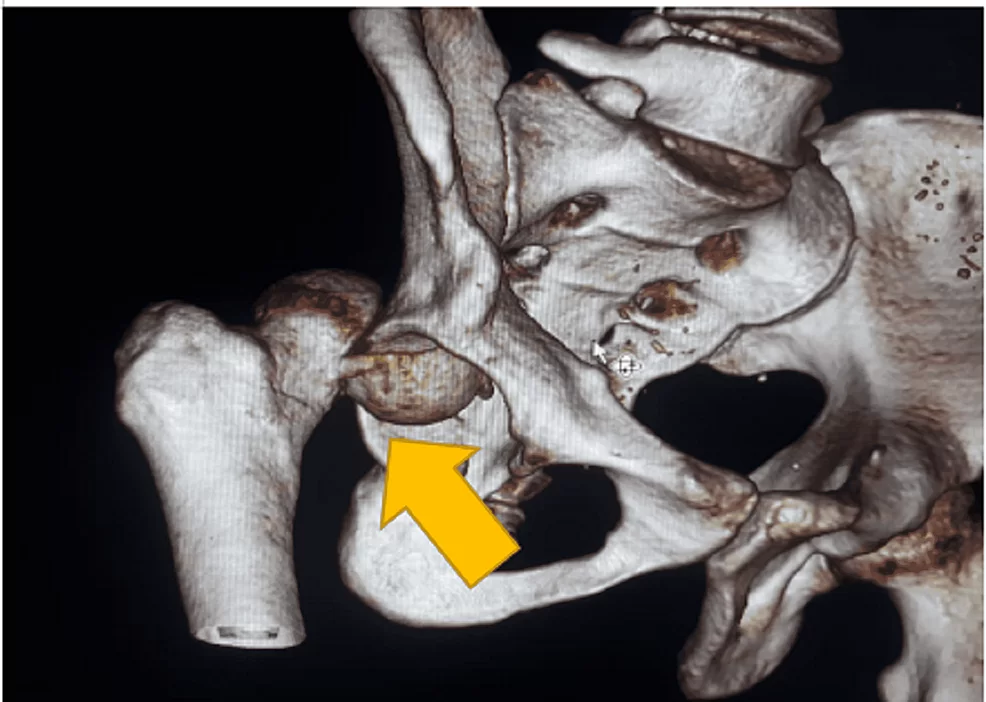
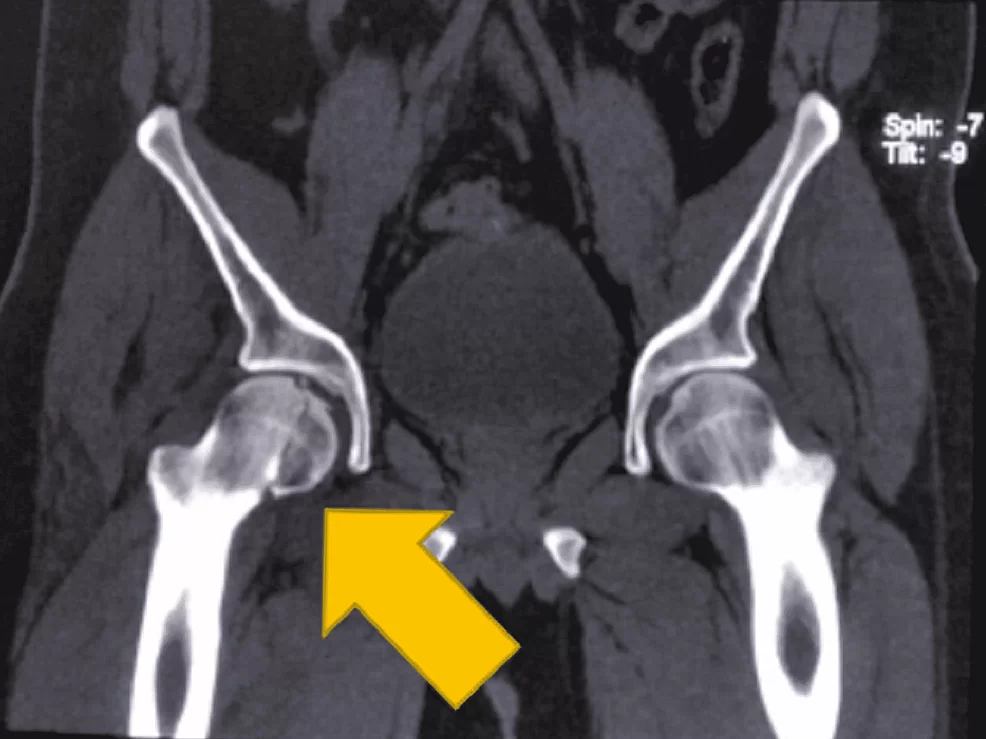
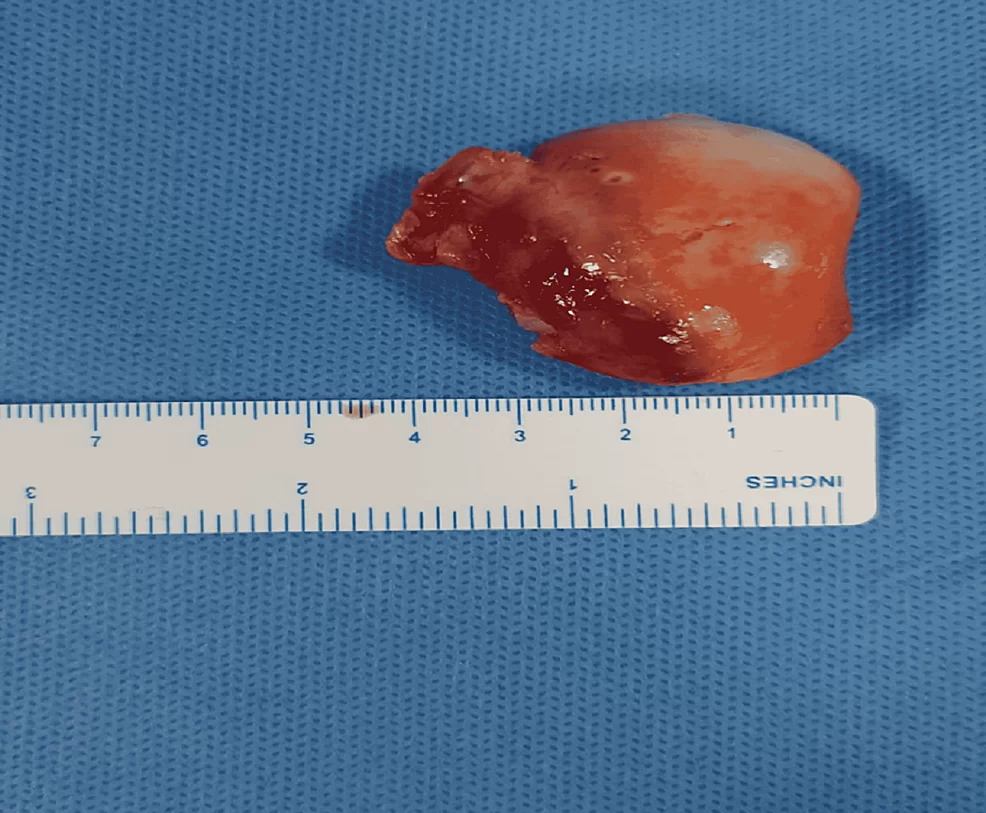
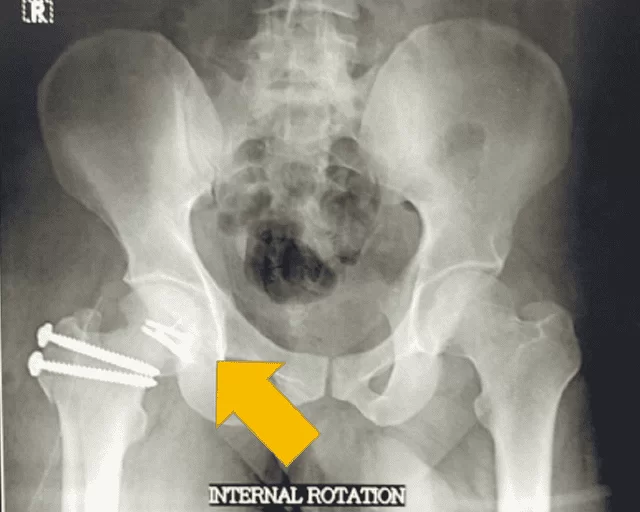
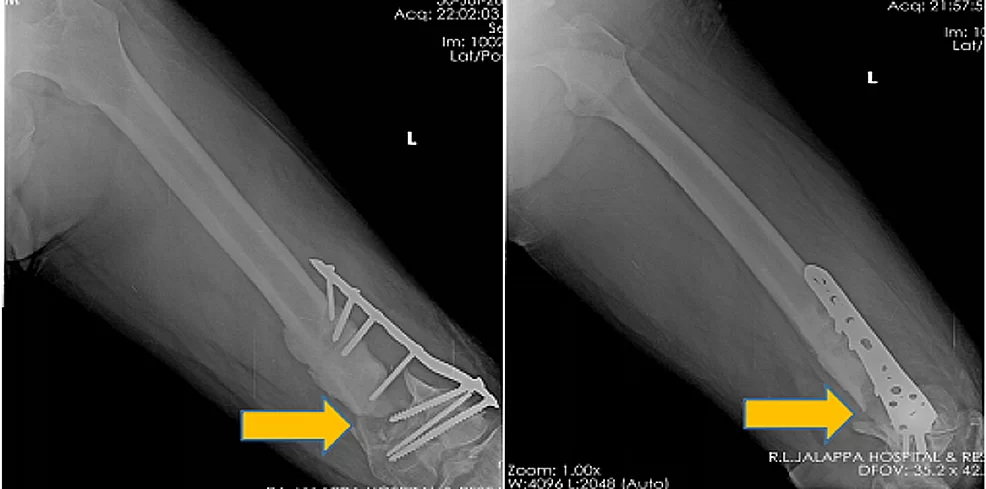
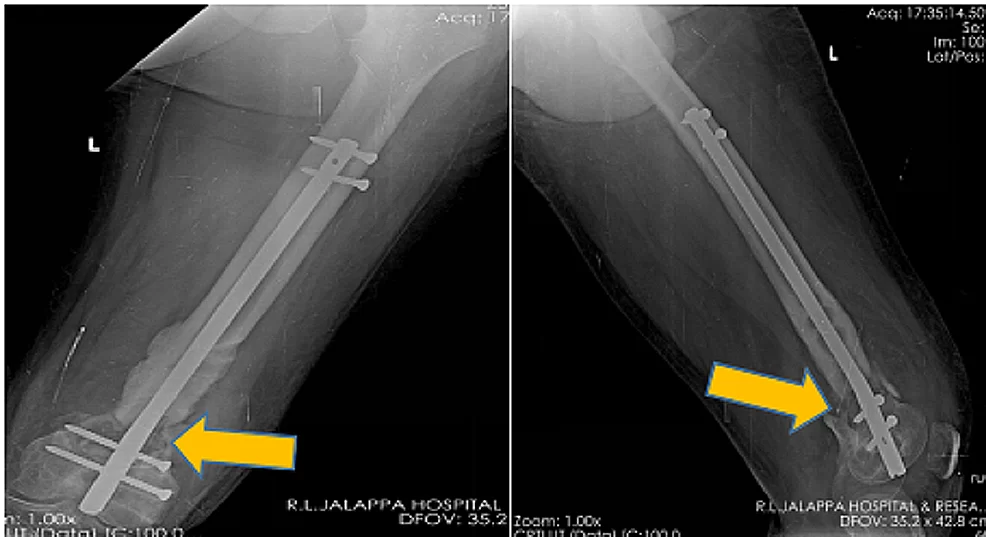
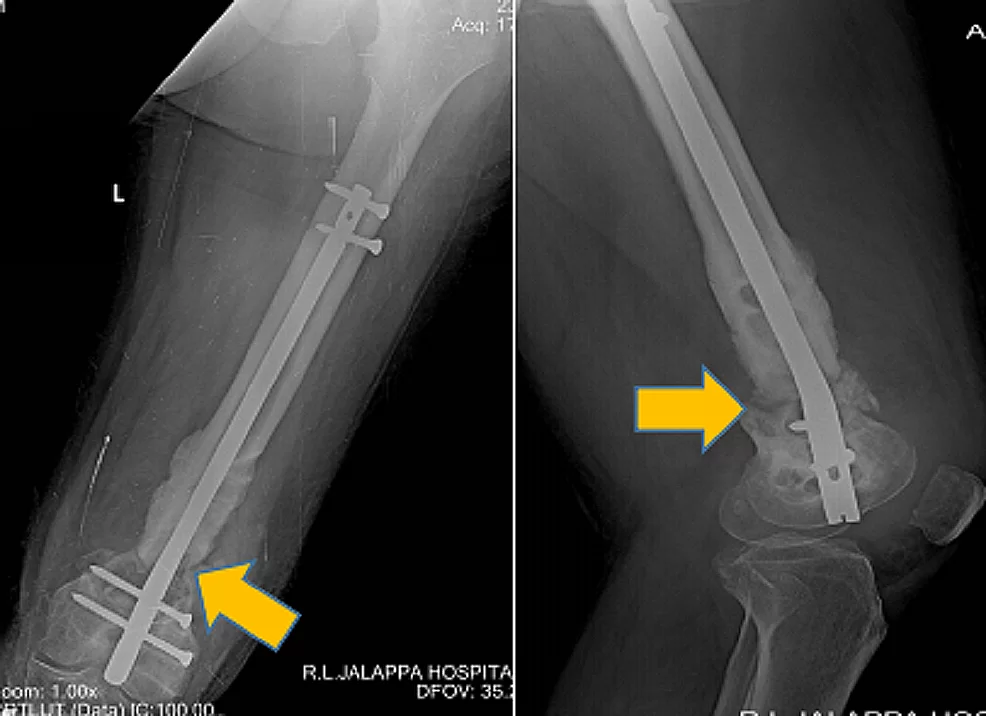
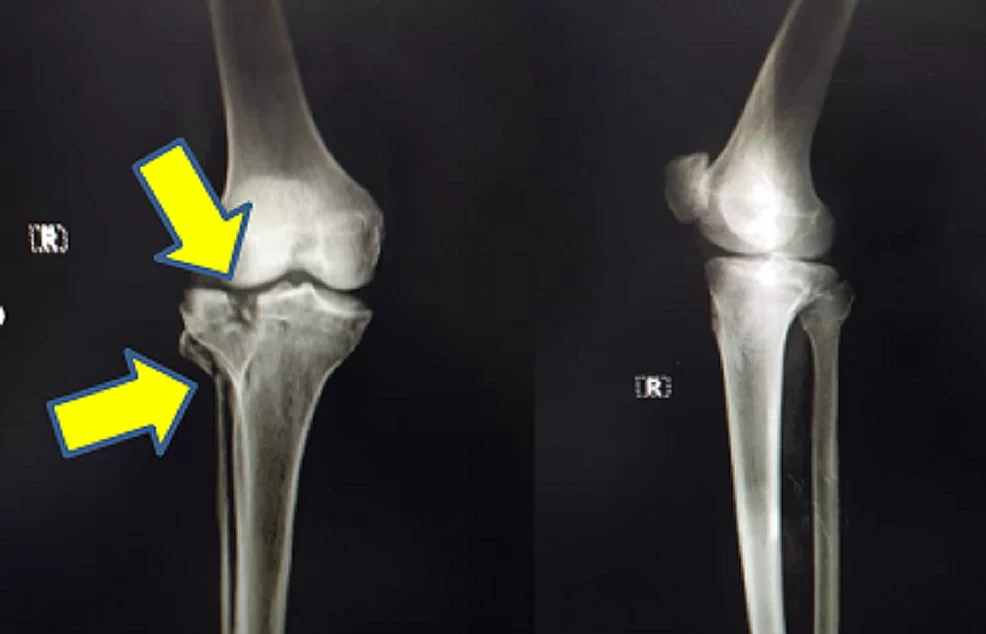
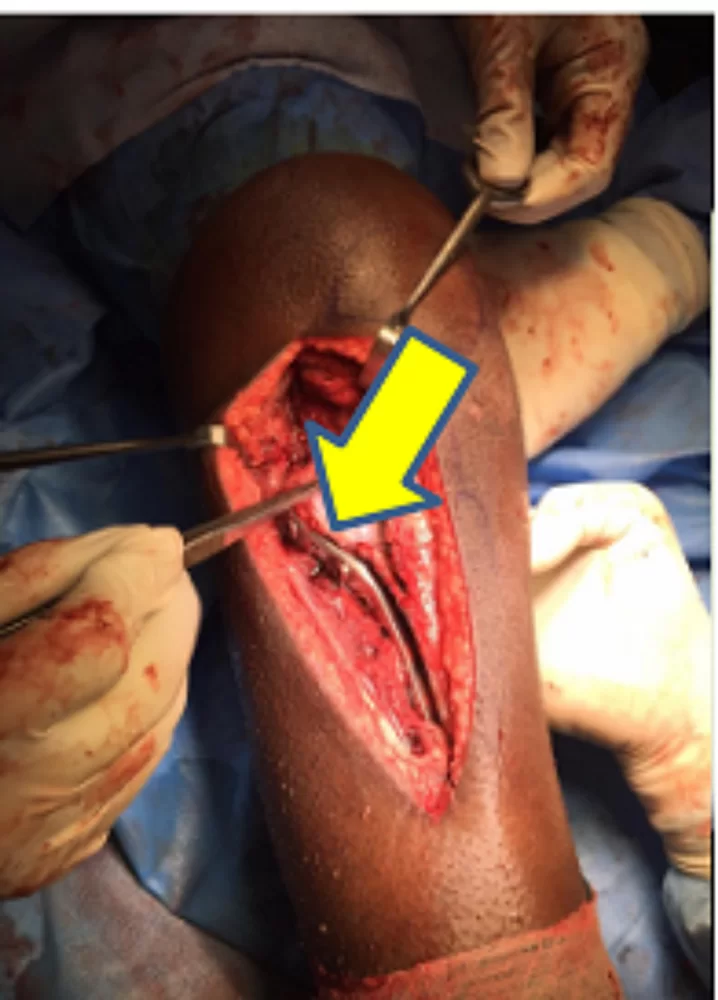
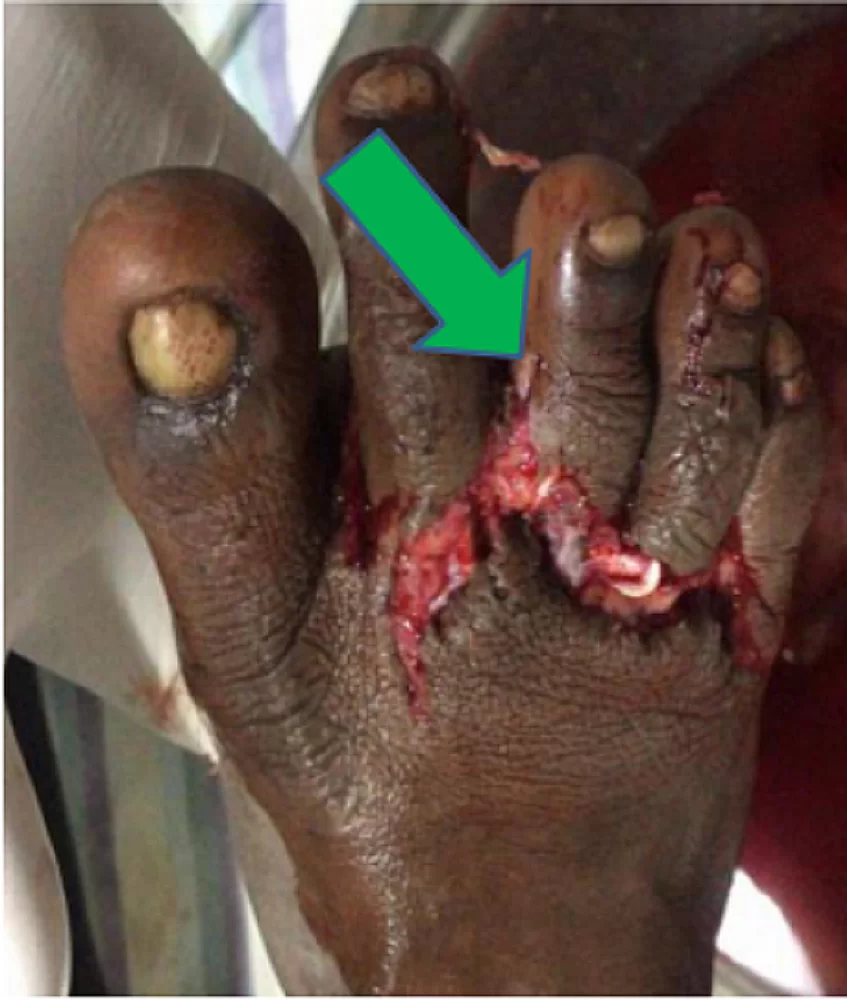
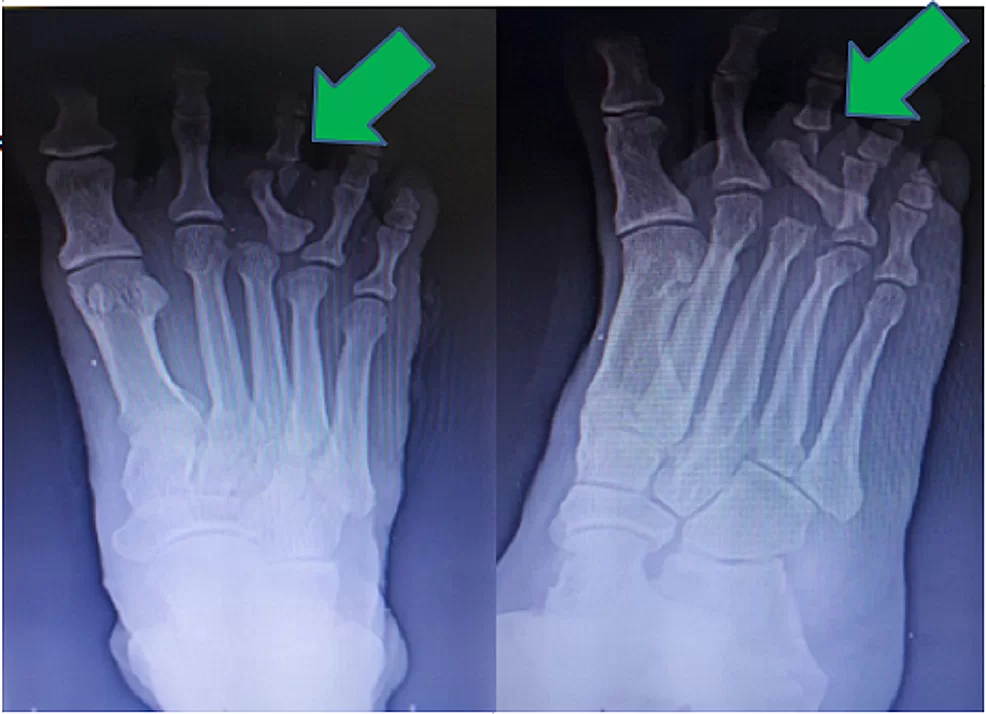
The Department of Orthopaedics was established at R.L. Jalappa Hospital and Research Centre in 1988 and has progressed well from its initial stages, to a fully equipped department with skilled faculty providing compressive trauma care and sub-speciality services. The Dept. has 3 Units and each unit has 2 OPD along with speciality clinics and 2 OT days per week.
Orthopaedic wards have total bed strength of 110. We have exclusive Orthopaedic operation theatres with laminar air flow, with C-Arm’s and all the required instrumentation and implants.
It is an honor and privilege to serve as Chair for our storied Department. Our rich history provides a solid foundation for us to further grow our Mission. With reverence to our past, we are looking to our future as leaders of musculoskeletal health care. Earlier this year, the faculty developed a strategic plan to guide us for the next five years. We have quite an ambitious agenda and need support to realize all we would like to do to grow and enhance our mission.
Our department includes fellowship-trained subspecialists in all major areas of orthopedic surgery, including arthroplasty, foot and ankle, spine, pelvis and acetabular surgeries, sports medicine, and orthopedic oncology. Additionally, our team includes highly trained physicians specializing in non-operative treatment of musculoskeletal ailments and injuries. We pride ourselves on a multidisciplinary approach to ensure every one of our patients receives personalized care tailored to their condition and circumstance.
The Department of Orthopedic Surgery is not only committed to providing expert care today but is also dedicated to discovering the most effective musculoskeletal treatments of tomorrow. Every year, eight promising medical students are selected from a pool of over thousands of NEET passed candidates to enter into our three-year comprehensive Orthopaedic surgery training program. Our dedicated faculty are committed to ensuring that future surgeons are prepared to provide the highest level of care to meet their patients' needs in an ever-changing and complex health care system.
When you receive treatment at R L Jalappa hospital and research Centre, your healthcare team will stand by you from diagnosis through post-operative care. Thanks to our residents, physical therapists, social workers, and other specialized doctors, we are poised to lead you on the road to recovery. With a dedication to your long-term well-being, our team will be with you every step of the way as you make your transition from treatment at R L Jalappa hospital and research Centre to your return home and back to your daily life.